Terrestrial Ecotoxicology
Our expert team is able to provide testing services on terrestrial non-target organisms according to requirements in the Regulations for the Registration of Plant Protection Products, Biocides (BPR), Chemicals (REACH), Veterinary Drugs and Pharmaceuticals. The studies are GLP compliant and the experimental designs reflect the most updated testing guidelines (OECD, IOBC/WPRS).
Discover our tests on:
No target arthropods
IOBC/WPRS Guideline (2000): Predatory mite – Thyphlodromus piry Scheuten
The predatory mite Thyphlodromus piry was chosen as non-target arthropod (NTA) standard specie since it proved to be the most sensitive in a range of experiments carried out on different species of NTA with many different Plant Protection Products.
Protonymphs 24 hours old, are exposed to the test substance applied on glass plate (laboratory test) or on natural surface as plants or parts of plants (extended laboratory test) in order to evaluate the effects in terms of mortality over 7 days exposure period and sub-lethal effects in terms of viability of surviving females over the following 7 days.
TEST SYSTEM
Thyphlodromus piry protonymphs 24 hours old.

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding is carried out with at least 3 application rates of the test substance and 1 untreated control (3 replicates/treatment or control) with 20 mites/replicate.
Limit test includes 1 application rate of the test substance, 1 untreated control and 1 toxic reference treatment (5 replicates/treatment or control) with 20 mites/replicate.
Rate-response test includes at least 5 application rates of the test substance, 1 untreated control and 1 toxic reference treatment (3 replicates/treatment or control) with 20 mites/replicate.
In order to evaluate the duration of the effects of the test substance and the recovery capacity of the insects it is possible to carry out an extended laboratory test with aged residues of the test substance.
The plants are treated in semi-field conditions and the leaves of the treated plants, after an adequate aging time, are moved to laboratory to perform the standard test as previously described.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: NOER/LR50 at 7 days after treatment.
Reproduction capacity: NOER/ER50 from 7 days to 14 days after treatment.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
IOBC/WPRS Guidelines (Mead-Briggs et al., 2000).
ESCORT I Guidance Document (Barret K.L. et al., eds. 1994).
ESCORT II Guidance Document (Candolfi et al., eds. 2001).
ESCORT 3 (Setac publication, 2010).
IOBC/WPRS Guideline (2000): Parasitic wasp – Aphidius rhopalosiphi
The parasitic wasp Aphidius rhopalosiphi was chosen as non-target arthropod (NTA) standard specie since it proved to be the most sensitive in a range of experiments carried out on different species of NTA with many different Plant Protection Products.
Parasitoids adults, less than 48 hours old, are exposed to different concentrations of the test substance applied on glass plate (laboratory test) or on natural surface as plants or plants parts by a calibrated spray equipment, in order to evaluate the effects in terms of mortality over 48 hours exposure period and sub-lethal effects in terms of reproduction capacity of surviving females (10-12 days).
TEST SYSTEM
Adults of Aphidius rhopalosiphi

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding is carried out with at least 3 application rates of the test substance and 1 untreated control (3 replicates/treatment or control) with 10 adults/replicate.
Limit test includes 1 application rate of the test substance, 1 untreated control and 1 toxic reference treatment (5 replicates/treatment or control) with 10 adults/replicate.
Rate-response test includes at least 5 application rates of the test substance, 1 untreated control and 1 toxic reference treatment (3 replicates/treatment or control) with 10 adults/replicate.
In order to evaluate the duration of the effects of the test substance and the recovery capacity of the insects it is possible to carry out an extended laboratory test with aged residues of the test substance.
The plants are treated in semi-field conditions and the leaves of the treated plants, after an adequate aging time, are moved to laboratory to perform the standard test as previously described.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LR50/NOER at 48 hours after treatment.
Reproduction capacity of the surviving females: ER50/NOER.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
IOBC/WPRS Guidelines (Mead-Briggs et al., 2000).
Guideline of the ring-testing group (Mead-Briggs et al., 2009).
ESCORT I Guidance Document (Barret K.L. et al., eds. 1994).
ESCORT II Guidance Document (Candolfi et al., eds. 2001).
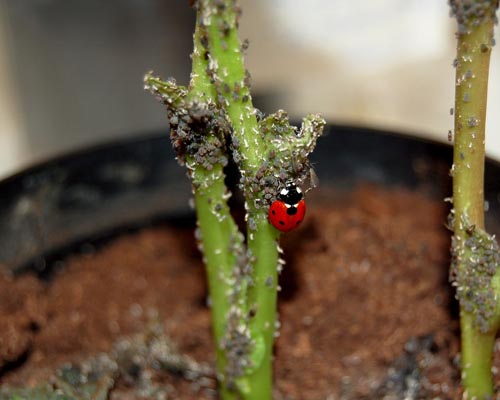
IOBC/WPRS Guideline (2000): Ladybird beetle – Coccinella septempunctata
The foliage dwelling insect Coccinella septempunctata is recommended as additional specie where the in-field or off-field risk assessment for the 2 standard species fails.
Ladybird beetle larvae are exposed to different concentrations of the test substance, applied on glass plates (laboratory test) or plant leaves (extended laboratory), by calibrated spray equipemnt, until the hatching of the adults in order to evaluate the effects in terms of mortality over the exposure period and the reproduction performance of the adults in terms of egg deposition and larval hatching rate over the following 2 weeks.
TEST SYSTEM
Larvae of Coccinella septempunctata

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding is carried out with at least 3 application rates of the test substance and 1 untreated control (at least 15 replicates/treatment or control) with 1 larva/replicate.
Limit test includes 1 application rate of the test substance, 1 untreated control and 1 toxic reference treatment (40 replicates/treatment or control) with 1 larva/replicate.
Rate-response test includes at least 5 application rates of the test substance, 1 untreated control and 1 toxic reference treatment (30 replicates/treatment or control) with 1 larva/replicate.
In order to evaluate the duration of the effects of the test substance and the recovery capacity of the insects it is possible to carry out an extended laboratory test with aged residues of the test substance.
The plants are treated in semi-field conditions and the leaves of the treated plants, after an adequate aging time, are moved to laboratory to perform the standard test as previously described.
ENDPOINTS
Pre-imaginal mortality: NOER/LR50 over the exposure period.
Reproductive performance: NOER/ER50 for eggs production and for eggs fertility over 2 weeks following the exposure.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
IOBC/WPRS Guidelines (Mead-Briggs et al., 2000).
ESCORT I Guidance Document (Barret K.L. et al., eds. 1994).
ESCORT II Guidance Document (Candolfi et al., eds. 2001).
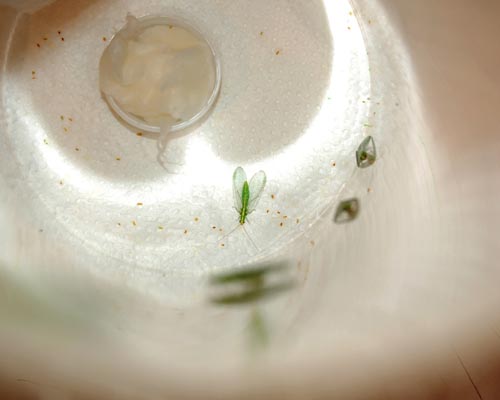
IOBC/WPRS Guideline (2000): Green lacewing – Chrysoperla carnea
The foliage dwelling insect Chrysoperla carnea is recommended as additional specie where the in-field or off-field risk assessment for the 2 standard species fails.
First instar larvae of the green lacewing, 2-3 days old, are exposed to the test substance applied on glass plate (laboratory test) or on natural surface (plants or plants parts), in order to evaluate the effects in terms of pre-imaginal mortality and reproduction performance of the adults. After treatment, larvae are transferred in to the test units. In the following days food is supplied. The surviving larvae are checked regularly. Cocoons are collected before hatching of the adults. All adults, based on the group treatments, are placed together for the reproductive assessment that starts one week after the first eggs were laid. The eggs are incubated for hatching in containers to determine their viability.
TEST SYSTEM
First instar larvae of Chrysoperla carnea

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding is carried out with at least 3 application rates of the test substance and 1 untreated control (at least 15 replicates/treatment or control) with 1 larva/replicate.
Limit test includes 1 application rate of the test substance, 1 untreated control and 1 toxic reference treatment (40 replicates/treatment or control) with 1 larva/replicate.
Rate-response test includes at least 5 application rates of the test substance, 1 untreated control and 1 toxic reference treatment (30 replicates/treatment or control) with 1 larva/replicate.
In order to evaluate the duration of the effects of the test substance and the recovery capacity of the insects it is possible to carry out an extended laboratory test with aged residues of the test substance.
The plants are treated in semi-field conditions and the leaves of the treated plants, after an adequate aging time, are moved to laboratory to perform the standard test as previously described.
ENDPOINTS
Pre-imaginal mortality: NOER/LR50 over the exposure period.
Reproductive performance: NOER/ER50 for eggs production/female per day and hatching rate.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
IOBC/WPRS Guidelines (Mead-Briggs et al., 2000).
ESCORT I Guidance Document (Barret K.L. et al., eds. 1994).
ESCORT II Guidance Document (Candolfi et al., eds. 2001).
IOBC/WPRS Guideline (2000): Rove beetle – Aleochara bilineata
The ground dwelling insect Aleochara bilineata is recommended in the cases of solid formulations incorporated as such in the soil or formulations to be applied as spray on soil.
Adult beetles, between 1 and 7 days after hatching from Delia antiqua pupae, are exposed to the test substance applied on quartz sand (laboratory test) or on natural standard soil (extended laboratory test) by spraying or by incorporation in order to evaluate the effects on their reproductive capacity. Ten pairs of adult males and females are placed on treated quartz sand. During the following 3 weeks 500 Delia antiqua pupae/week/replicate, are added to the test unit and after 4 weeks from the treatment the adult beetles are removed. The fly pupae are placed in to the hatching units and the effects in terms of reproduction ability over a period from 6 to 8 weeks are assessed recording the number of the newly emerged adult beetles.
TEST SYSTEM
Adults of Aleochara bilineata

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding is carried out with at least 3 application rates of the test substance and 1 untreated control (at least 2 replicates/treatment or control) with 20 beetles/replicate.
Limit test includes 1 application rate of the test substance, 1 untreated control and 1 toxic reference treatment (4 replicates/treatment or control) with 20 beetles/replicate.
Rate-response test includes at least 5 application rates of the test substance, 1 untreated control and 1 toxic reference treatment (4 replicates/treatment or control) with 20 beetles/replicate.
In order to evaluate the duration of the effects of the test substance and the recovery capacity of the insects it is possible to carry out an extended laboratory test with aged residues of the test substance.
The soil is treated in semi-field conditions and, after an adequate aging time, is moved to laboratory to perform the standard test as previously described.
ENDPOINTS
Reproduction performance: ER50/NOER or EC50/NOEC in terms of mean number of offsprings/beetle,
as option, mortality and behavioural effects are observed.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
IOBC/WPRS Guidelines (Mead-Briggs et al., 2000).
ESCORT I Guidance Document (Barret K.L. et al., eds. 1994).
ESCORT II Guidance Document (Candolfi et al., eds. 2001).
IOBC/WPRS Guideline (2000): Carabid beetle – Poecilus cupreus
The ground dwelling insect Poecilus cupreus is recommended in the cases of solid formulations incorporated as such in the soil or formulations to be applied as spray on soil.
Adult beetles, from 4 to 9 weeks old, are exposed to the test substance applied on quartz sand (laboratory test) or sandy standard soil (extended laboratory) by spraying or by incorporation. For at least 3 days before the test starts, the beetles are kept without food and acclimatised to the test conditions. Immediately before test substance application and during the test, fly pupae are placed into test system as food source. After 2 weeks of exposure the lethal effects are assessed and food consumption, together with behavioural abnormalities, are recorded.
TEST SYSTEM
Adults of Poecilus cupreus

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding is carried out with at least 3 application rates of the test substance and 1 untreated control (at least 2 replicates/treatment or control) with 6 beetles/replicate.
Limit test includes 1 application rate of the test substance, 1 untreated control and 1 toxic reference treatment (5 replicates/treatment or control) with 6 beetles/replicate.
Rate-response test includes at least 5 application rates of the test substance, 1 untreated control and 1 toxic reference treatment (5 replicates/treatment or control) with 6 beetles/replicate.
In order to evaluate the duration of the effects of the test substance and the recovery capacity of the insects it is possible to carry out an extended laboratory test with aged residues of the test substance.
The soil is treated in semi-field conditions and, after an adequate aging time, is moved to laboratory to perform the standard test as previously described.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LR50 after 14 days of exposure period.
Food consumption: ECx/NOEC.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
IOBC/WPRS Guidelines (Mead-Briggs et al., 2000).
ESCORT I Guidance Document (Barret K.L. et al., eds. 1994).
ESCORT II Guidance Document (Candolfi et al., eds. 2001).
ESCORT 3 (Setac publication, 2010).
Bees
OECD TG 213: Honeybees, Acute Oral Toxicity test
Agriculture provides habitat and forage for pollinating insects such as honey bees.
As well as producing honey and a variety of hive products, honey bees perform the ecosystem service of pollination which allows plants to reproduce, provides the fruits, seeds and foliage.The use of plant protection product in agriculture leads to exposure of honey bees to pesticide residues. The oral exposure comes mainly from pollen and nectar consumption from the treated crops, from the weeds in treated field, from plants in field margins and from the adjacent crops where the liquid or solid particles resulting from spray/dust drift might be present.
A minor route of exposure to take into account derived from water consumption in terms of guttation fluids, surface waters and ponds.
Adult worker honeybees are exposed to the test substance dispersed in the diet (sucrose solution) in order to evaluate the mortality and sublethal effects. Mortality and sublethal effects are assessed at 4, 24 and 48 hours after the administration of contaminated diet. If an extention is needed, further observations are carried out at 72 and 96 hours after the beginning of the test.
TEST SYSTEM
Adult honey bees of Apis mellifera L.

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 3 doses of the test substance and 1 untreated control, at least 2 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bees/replicate.
Limit test is carried out with 1 dose of the test substance, 1 toxic reference substance and 1 untreated control, 5 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bees/replicate.
Dose-response test includes at least 5 doses of the test substance, 1 toxic reference substance and 1 untreated control, 3 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bees/replicate.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LDx/NOED and behavioural abnormalities are recorded.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 213 (21st September 1998) – Honeybees, Acute oral toxicity test.
OECD TG 214: Honeybees, Acute Contact Toxicity test
Agriculture provides habitat and forage for pollinating insects such as honey bees.
As well as producing honey and a variety of hive products, honey bees perform the ecosystem service of pollination which allows plants to reproduce, provides the fruits and seeds.The use of plant protection product in agriculture leads to exposure of honey bees to pesticide residues. The exposure via contact occurs while honey bees are feeding from the treated crops, from the weeds in treated field, from plants in field margins and from the adjacent crops where the liquid or solid particles resulting from spray/dust drift might be present.
Adult worker honeybees are exposed to the test substance dissolved in appropriate carrier, by direct application to the thorax (droplets) in order to evaluate the mortality and sublethal effects. Mortality and sublethal effects are assessed at 4, 24 and 48 hours after the treatment. If an extention is needed, further observations are carried out at 72 and 96 hours after the beginning of the test.
TEST SYSTEM
Adult honey bees of Apis mellifera L.

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 3 doses of the test substance and 1 untreated control, at least 2 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bees/replicate.
Limit test is carried out with 1 dose of the test substance, 1 toxic reference substance and 1 untreated control, 5 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bees/replicate.
Dose-response test includes at least 5 doses of the test substance, 1 toxic reference substance and 1 untreated control, 3 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bees/replicate.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LDx/NOED and behavioural abnormalities are recorded.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 214 (21st September 1998) – Honeybees, Acute contact toxicity test.
OECD Guidance Document No 239 on Honey bee Larval Toxicity Test following Repeated Exposure
Agriculture provides habitat and forage for pollinating insects such as honey bees.
As well as producing honey and a variety of hive products, honey bees perform the ecosystem service of pollination which allows plants to reproduce, provides the fruits and seeds.The use of plant protection product in agriculture leads to exposure of honey bees to pesticide residues.
Honeybee larvae are collected from at least 3 healthy colonies with known history and physiological status. Queens are confined in their colonies in exclusion cages with empty combs, after 1 day the queens are released and the laid eggs are left in the cages inside the hives until hatching. The combs, containing first instars larvae, are transferred from hives to laboratory. On day 1, larvae are grafted on crystal polystyrene grafting cells, containing the diet. From day 3 to day 6 the test item is administered daily to the larvae with the diet. Mortality of larvae is assessed dailly after the first administration of contaminated diet (D4, D5, D6, D7 and D8). Mortality of the pupae is evaluated (D15). Cumulative mortality is assessed at the adult’s emergence time at the end of the test (D22).
TEST SYSTEM
Honey bee larvae of Apis mellifera L.

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 3 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control, at least 2 replicates for treatment and for the control with 12 larvae/replicate.
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration of the test substance, 1 toxic reference substance and 1 untreated control, 3 replicates for treatment and for the control with 12 larvae/replicate.
Dose-response test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance, 1 toxic reference substance and 1 untreated control, 3 replicates for treatment and for the control with 12 larvae/replicate.
Analytical check
Analytical check of the test substance stock solution is carried out at each administration time to verify the effective concentration of the test substance.
Analyses are carried out using a method validated according to SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance documents.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LCx/NOED on D8, D15 and D22.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guidance document on honeybee larval toxicity test following repeated exposure, Series on Testing and Assessment N. 239 (15th July 2016).
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
OECD TG 245: Honey bee (Apis mellifera L.), Chronic Oral Toxicity test (10-day feeding)
Agriculture provides habitat and forage for pollinating insects such as honey bees.
As well as producing honey and a variety of hive products, honey bees perform the ecosystem service of pollination which allows plants to reproduce, provides the fruits and seeds.The use of plant protection product in agriculture leads to exposure of honey bees to pesticide residues. The need to carry out 10-day chronic oral test on adult honey bees derives from the fact that acute oral and contact toxicity tests not allow to take into account the potential chronic exposure to pesticides in-hive, a very different scenario from the time-limited exposure in the field simulated in acute laboratory test.
Young worker honey bees, less than 2 days old, are exposed to the test substance by food supplied continuously and ad libitum over a period of 10 days to evaluate chronic effects. 2 days before the test starting, brood frames with capped cells are taken from the hive and incubated in climatic chambers until hatching. One day before the test starting, hatched bees are collected from the combs and distributed in the test cages. Bees are acclimatized to test conditions for 1 day. The food consumption is recorded each day by weighing the feeders before and after the administration of 24 hours. Mortality and behavioural anomalies are observed and recorded daily during the test period.
TEST SYSTEM
Honey bee young workers of Apis mellifera L.
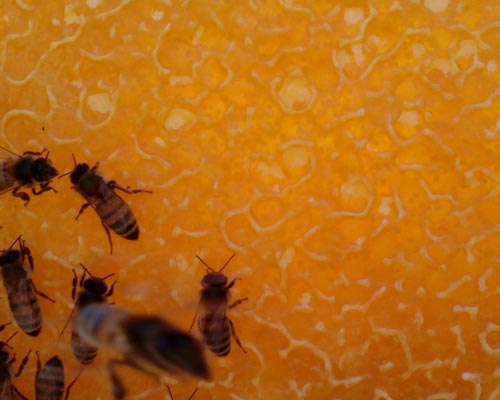

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 3 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control, at least 2 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bees/replicate.
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration of the test substance, 1 toxic reference substance and 1 untreated control, 5 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bees/replicate.
Dose-response test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance, 1 toxic reference substance and 1 untreated control, 3 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bees/replicate.
Analytical check
Once during the experimental phase, 1 sample of the lowest concentration and 1 sample of the highest concentration of the stock and the feeding solutions are analyzed to determine the effective concentration of the test substance.
Analyses are carried out using a method validated according to SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance documents.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LCx/LDDx and NOEC/NOEDD and LOEC/LOEDD after 10 days of treatment.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 245 (09th October 2017) – Honey bee (Apis mellifera L.), chronic oral toxicity test (10-day feeding)
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
Bumblebees
OECD TG 246: Bumblebee, Acute Contact Toxicity test
Bumblebees are social insects and live in small annual-cycle colonies.
Agriculture provides habitat and forage for pollinating insects, the ecosystem service of pollination allows plants to reproduce and bumblebees are sometimes used as pollinators in greenhouses where certain crops can be grown in controlled and specific conditions. The use of plant protection product in agriculture leads to exposure of pollinators to pesticide residues, so their effects on such insects has to be assessed.
Adult worker bumblebees are exposed to different concentrations of the test substance dissolved in appropriate carrier, by direct application to the thorax (droplets) in order to evaluate the mortality and sublethal effects. Bumblebees are collected from the hives and transferred into group-housing cages. In the acclimation period (12- 24 hours) at the test conditions, bumblebees are fed with aqueous sucrose solution ad libitum and, just before the test starting, they are treated by dorsal application. Mortality and sublethal effects are assessed daily until 72 hours after the treatment. If an extention is needed, further observations are carried out at 96 hours after the beginning of the test.
TEST SYSTEM
Adult bumblebees of Bombus terrestris
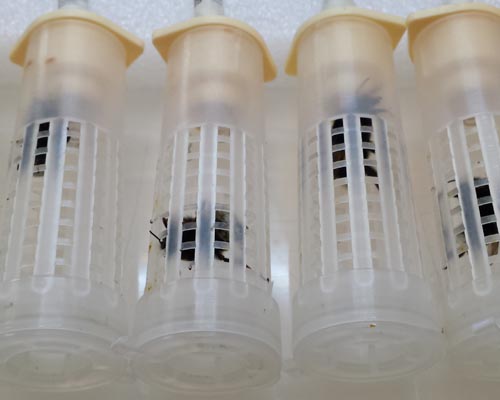

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 3 doses of the test substance and 1 untreated control, 3 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bumlebees/replicate.
Limit test is carried out with 1 dose of the test substance, 1 toxic reference substance and 1 untreated control, 5 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bumblebees/ replicate.
Dose-response test includes at least 5 doses of the test substance, 1 toxic reference substance and 1 untreated control, 3 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bumblebees/replicate.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LD50/NOED at 24, 48 and 72 hours after treatment and behavioural abnormalities are recorded.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 246 (09th Octoober 2017) – Bumblebee, Acute contact toxicity test.
OECD TG 247: Bumblebee, Acute Oral Toxicity test
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 246 (09th Ocrober 2017) – Bumblebee, Acute contact toxicity test.
Bumblebees are social insects and live in small annual-cycle colonies.
Agriculture provides habitat and forage for pollinating insects, the ecosystem service of pollination allows plants to reproduce and bumblebees are sometimes used as pollinators in greenhouses where certain crops can be grown in controlled and specific conditions. The use of plant protection product in agriculture leads to exposure of pollinators to pesticide residues, so their effects on such insects has to be assessed.
Adult worker bumblebees are exposed to the test substance dispersed in the aqueous sucrose solution in order to evaluate the mortality and sublethal effects. Bumblebees are collected from the hives in a dark room under red light they are transferred into single-housing cages. After the acclimatation period (12- 24 hours) at the test conditions, bumblebees are starved for 2 hours before the exposure takes place by the feeders containing the treated diet. Mortality and sublethal effects are assessed daily until 72 hours after the treatment. If an extention is needed, further observations are carried out at 96 hours after the beginning of the test.
TEST SYSTEM
Adult bumblebees of Bombus terrestris
STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 3 doses of the test substance and 1 untreated control, 3 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bumblebees/replicate.
Limit test is carried out with 1 dose of the test substance, 1 toxic reference substance and 1 untreated control, 5 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bumblebees/replicate.
Dose-response test includes at least 5 doses of the test substance, 1 toxic reference substance and 1 untreated control, 3 replicates for treatment and for the control with 10 bumblebees/replicate.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LD50/NOED at 24, 48 and 72 hours.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 247 (09th October 2017) – Bumblebee, Acute oral toxicity test.
Soil macro and microorganisms
OECD TG 207: Earthworm, Acute Toxicity test
Earthworms have the ability to mix soil layers and to incorporate organic matter into the soil, therefore the organic matter can be released through the soil and its nutrients can become available to bacteria, fungi and plants increasing soil fertility.
Reproductive adult earthworms of Eisenia andrei, are exposed to the test substance incorporated into the artificial soil by an appropriate carrier or sprayed on the soil surface in order to evaluate the effects in terms of mortality and reduction in body weight over 14 days exposure period.
TEST SYSTEM
Eisenia andrei
A toxic reference substance is tested once a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.
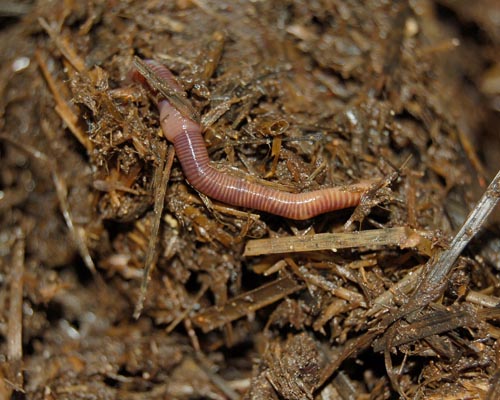

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (at least 2 replicates/treatment or control) with 10 adults/replicate
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration of the test substance and 1 untreated control (4 replicates/treatment or control) with 10 adults/replicate
Rate-response test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (4 replicates/treatment and for the control) with 10 adults/replicate
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LC50 at 7 days and at 14 days after treatment.
Reduction in body weight: EC50 at 14 days after treatment.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 207 (4th April 1984) – Earthworm, acute toxicity test.
OECD TG 222: Earthworm Reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei)
Effects data on earthworms are required for each active substance or formulated product unless it is proved that, based on its intended use, the active substance can not reach the soil.
Reproductive adult earthworms of Eisenia andrei, are exposed to the test substance incorporated into the artificial soil by an appropriate carrier or sprayed on the soil surface in order to evaluate the lethal and sub-lethal (as reproduction and weight losses) effects. Mortality and reduction in body weight are assessed after 4 weeks of exposure and the reproduction capacity is evaluated 4 weeks following the end of the exposure period for an overall test duration of 8 weeks.
TEST SYSTEM
Eisenia andrei
A toxic reference substance is tested once a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.
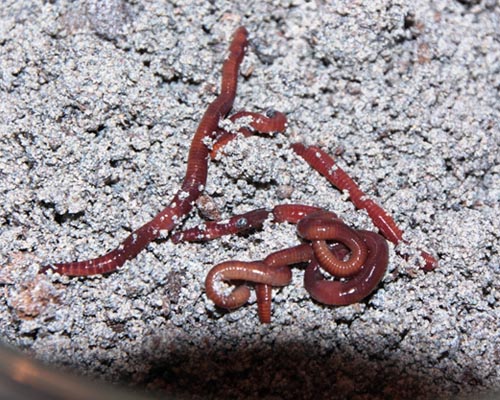

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test lasts for 2-4 weeks and it includes 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (2 replicates/treatment or control) with 10 adults/replicate
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration of the test substance and 1 untreated control (8 replicates/treatment or control) with 10 adults/replicate
Rate-response test for NOEC evaluation includes from 5 to 12 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (4 replicates/treatment and 8 replicates for the control) with 10 adults/replicate.
Rate-response test for ECx evaluation includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (at least 2 replicates/treatment and 6 replicates for the control) with 10 adults/replicate.
Rate-response test for ECx and NOEC/LOEC evaluation is performed with 8 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (4 replicates/treatment and 8 replicates for the control) with 10 adults/replicate.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LCx and/or NOEC after 4 weeks of exposure.
Weght change: ECx and/or NOEC after 4 weeks of exposure.
Reduction in reproduction: ECx and/or NOEC at the end of the test (8 weeks).
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 222 (29th July 2016) – Earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei).
OECD TG 232: Collembolan Reproduction test in soil
Soil-dwelling Collembola are ecologically relevant species for ecotoxicological testing.
Collembolans are hexapods with a thin exoskeleton highly permeable to air and water, and represent arthropod species with a different route and a different rate of exposure compared to earthworms and enchytraeids.
Synchronized female of Folsomia candida, 9-12 days old, are exposed to the test substance incorporated into the artificial soil by an appropriate carrier or sprayed on the soil surface in order to evaluate the lethal and reproduction effects. Mortality and reproduction performance are assessed after 4 weeks of exposure.
TEST SYSTEM
Folsomia candida
A toxic reference substance is tested once a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.
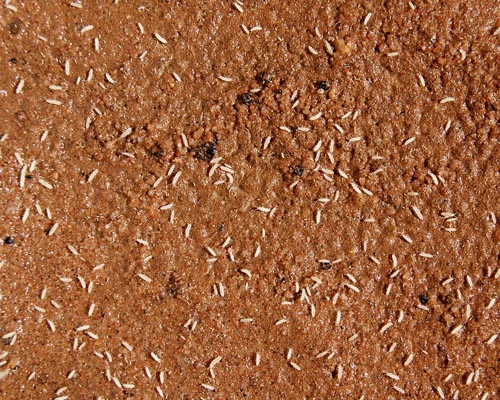

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test lasts for 3 weeks and it includes 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (2 replicates/treatment or control) with 10 females/replicate
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration of the test substance and 1 untreated control (8 replicates/treatment or control) with 10 females/replicate
Rate-response test for NOEC/LOEC evaluation includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (4 replicates/treatment and 8 replicates for the control) with 10 females/replicate.
Rate-response test for ECx evaluation includes 12 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (at least 2 replicates/treatment and 6 replicates for the control) with 10 females/replicate.
Rate-response test for ECx and NOEC/LOEC evaluation is performed with 8 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (4 replicates/treatment and 8 replicates for the control) with 10 females/replicate.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LCx or LOEC/NOEC after 4 weeks of exposure.
Reduction in reproduction: ECx or NOEC/LOEC after 4 weeks of exposure.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 232 (29th July 2016) – Collembolan reproduction test in soil.
OECD TG 226: Predatory mite (Hypoaspis (Geolaelaps) aculeifer) Reproduction test in soil
Hypoaspis (Geolaelaps) aculeifer is considered to be a relevant representative of soil fauna and predatory mites in particular. It is worldwide distributed and can easily be collected and reared in the laboratory.
Synchronized adult females of Hypoaspis aculeifer, of 28-35 days after the start of egg lying period, are exposed to the test substance mixed into the artificial soil by an appropriate carrier or sprayed on the soil surface in order to evaluate the effects on reproduction and other sublethal effects. Reproduction performance is assessed after 2 weeks of exposure.
TEST SYSTEM
Hypoaspis (Geolaelaps) aculeifer
A toxic reference substance is tested once a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.
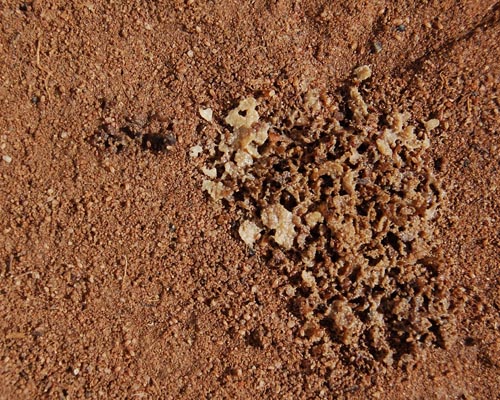

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (2 replicates/treatment or control) with 10 females/replicate.
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration of the test substance and 1 untreated control (8 replicates/treatment or control) with 10 females/replicate.
Rate-response test for NOEC/LOEC evaluation includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (4 replicates/treatment and 8 replicates for the control) with 10 females/replicate.
Rate-response test for ECx evaluation includes 12 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (at least 2 replicates/treatment and 6 replicates for the control) with 10 females/replicate.
Rate-response test for ECx and NOEC/LOEC evaluation is performed with 8 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (4 replicates/treatment and 8 replicates for the control) with 10 females/replicate.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LCx or LOEC/NOEC after 2 weeks of exposure.
Reduction in reproduction: ECx or NOEC/LOEC after 2 weeks of exposure.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 226 (29th July 2016) – Predatory mite (Hypoaspis (Geolaelaps) aculeifer) reproduction test in soil.
OECD TG 216: Soil Microorganisms: Nitrogen Transformation test
Standard soil with specific characteristics is amended with a suitable organic substrate and mixed directly, or by an appropriate carrier, with different concentrations of the test substance in order to evaluate the effects on microbial nitrate formation rate. The deviation (%) in nitrate formation rate respect to the untreated soil control is assessed at defined intervals until 28 days after the treatment or for a maximum of 100 days until a difference ≤ 25 % is obtained.
TEST SYSTEM
Agricultural loamy sand soil.
A toxic reference substance is tested once a year to check the sensitivity of the soil microoorganisms.
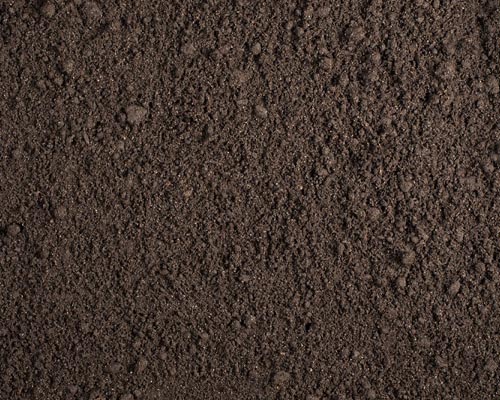

STUDY DESIGN
For agrochemicals products 2 concentrations and 1 untreated control are tested
(3 replicates/concentration and for the control).
For substances other than agrochemicals, a dose-response test for ECx evaluation is carried out. It includes at least 5 concentrations and 1 untreated control (3 replicates/concentration and for the control).
ENDPOINTS
% of deviation in nitrate formation rate of treated soils respect to the untreated soil, at the end of the test.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 216 (21st January 2000) – Soil microorganisms: Nitrogen transformation test.
OECD TG 217: Soil microorganisms: Carbon Transformation test
Standard soil with specific characteristics is mixed directly, or by an appropriate carrier,with different concentrations of the test substance in order to evaluate the effects on glucose induced respiration rate of the soil microorganims (measured for 12 consecutive hours). The deviation (%) in respiration rate respect to the untreated soil control is assessed at defined intervals until 28 days after the treatment or for a maximum of 100 days until a difference ≤ 25 % is obtained.
TEST SYSTEM
Agricultural loamy sand soil
A toxic reference substance is tested once a year to check the sensitivity of the soil microoorganisms.

STUDY DESIGN
For agrochemicals products 2 concentrations and 1 untreated control are tested
(3 replicates/concentration and for the control).
For substances other than agrochemicals, a dose-response test for ECx evaluation is carried out. It includes at least 5 concentrations and 1 untreated control (3 replicates/concentration and for the control).
ENDPOINTS
% of deviation in soil respiration rate of treated soils respect to the untreated soil at the end of the test.
Study includes GLP management and reporting
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 217 (21st January 2000) – Soil microorganisms: Carbon transformation test.
No target plants
OECD TG 208: Terrestrial Plant Test: Seedling Emergence-Seedling Growth test
Seeds from at least 6 plant species, are exposed to the test substance, either incorporated into the soil or sprayed to the soil surface by appropriate carrier, to assess the effects on seedling emergence and on early growth of higher plants. Seedling emergence and mortality are assessed at 14 and 21 days after the emergence of seedlings in the untreated control group has reached 50%. The fresh shoot weight is measured at the end of the test (21 days).
TEST SYSTEM
Seeds belonging to different plant families of dicotyledonae and monocotyledonae including among others: Brassica napus, Lycopersicon esculentum, Beta vulgaris, Raphanus sativus, Lactuca sativa, Hordeum vulgare and Lolium perenne.

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test for each plant species includes at least 3 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control.
Limit test for each plant species is carried out with 1 concentration of the test substance and 1 untreated control.
Rate-response test for each plant species includes 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control.
Based on plant species used, for each test substance concentration and for the untreated control, 6/12 replicates with 4/2 seeds each one are required.
Analytical check
Stock solution is checked for test substance concentration/rate using an analytical method validated according to SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance document.
ENDPOINTS
Emergence %: ERx and NOER at the end of the test.
Mortality: LRx and NOER at the end of the test.
Biomass as fresh shoot weight: ERx and NOER at the end of the test.
Phytotoxicity: visual assessment at the end of the test.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 208 (19th July 2006) – Terrestrial plant test: seedling emergence and seedling growth test.
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
OECD TG 227: Terrestrial Plant Test: Vegetative Vigour test
At least 6 plant species from seeds (2 to 4 true leaves stage), are exposed to the test substance sprayed by a calibrated spray equipment in order to evaluate potential adverse effects. Mortality and phytotoxicity are assessed weekly until the end of the test (21 days after the treatment) and additionally fresh shoot weight is measured at test completion to evaluate effects on biomass.
TEST SYSTEM
Plant species belonging to different plant families of dicotyledonae and monocotyledonae including among others: Daucus carota, Brassica napus, Pisum sativum, Avena sativa, Zea mais, Allium cepa, Cucumis sativus, Helianthus annuus and Phaseolus vulgaris.

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test for each plant species includes at least 3 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control.
Limit test for each plant species is carried out with 1 concentration of the test substance and 1 untreated control.
Rate-response test for each plant species includes 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control.
Based on plant species used, for each test substance concentration and for the untreated control, 6/12 replicates with 4/2 plants each one are required.
Analytical check
Stock solution is checked for test substance concentration/rate using an analytical method validated according to SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance document.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LRx and NOER at the end of the test.
Biomass as fresh shoot weight: ERx and NOER at the end of the test.
Phytotoxicity: visual assessment at the end of the test.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 227 (19th July 2006) – Terrestrial plant test: vegetative vigour test.
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
Study finder
Sales and Scientific Contact
Monica Colli
E-mail: mcolli@biotecnologiebt.it
Phone: +39 075 895 0045 – Ext. 252
Discover the other Expertise
Didn’t find what you are looking for? Send us a message!
Fill in the form with the required information (*).
Our team will be happy to quickly provide all the necessary support with regard to your request


 English
English Italian
Italian