Aquatic Ecotoxicology
Studies on non-target organisms according to the most updated testing regulations
Our company is able to offer a wide range of GLP studies required by the current Regulations for the Registration of Plant Protection Products, Biocides (BPRs), Chemicals (REACH), Veterinary Drugs and Pharmaceuticals.

Propaedeutic Analytical evaluation
The analytical determination necessary to check the dose of the active substance in the biological system is carried out by our Chemical-Physical Unit.
Discover our tests on:
Aquatic plants
OECD TG 201: Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria
Exponentially growing test organisms (in house breeding at B.T.) in EPA medium are exposed to the test substance in batch cultures over a period of normally 72 hours to determine the effects of a test substance on the growth of freshwater green algae or cyanobacteria. The test is carried out in static system.
TEST SYSTEM
Green algae: Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata, Desmodesmus subspicatum
Cyanobacteria: Anabaena flos-aquae
A toxic reference substance is tested twice a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (3 replicates/concentration or control) with an adequate initial biomass concentration in terms of cells/mL for replicate.
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration (100 mg/L or at solubility limit) of the test substance and 1 untreated control (at least 6 replicates/concentration or control) with an adequate initial biomass concentration in terms of cells/mL for replicate.
Dose-response test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and
1 untreated control (3 replicates/concentration or control) with an adequate initial biomass concentration in terms of cells/mL for replicate.
Analytical checks, to verify the exposure concentrations in the medium, are performed at time 0 and at time 72 hours on control and on each test substance sample.
The analysis are performed using a method validated according to SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 and SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance documents.
ENDPOINTS
Inhibition of the growth rate and of the yield: EC10, EC20, EC50, NOEC/LOEC after 72 hours calculated by the cells number counting/mL.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 201 (23rd March 2006) – Annex 5 corrected: 28th July 2011) – Fresh Alga and Cyanobacteria, growth inhibition test.
OECD Series on Pesticides, Number 67: “OECD guidance to the environmental safety evaluation of microbial biocontrol agents” (17th February 2012).
Environmental Canada, EPS 1/RM/44: “Guidance Document for Testing the Pathogenicity and Toxicity of New Microbial Substances to Aquatic and Terrestrial Organisms” (March 2004).
SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 (16/11/2010) – Guidance document on pesticide residue analytical methods.
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
OECD TG 221: Lemna sp. Growth Inhibition test
Lemna sp. aquatic plants (in house breeding at B.T.) are exposed to a range of concentrations of the test substance in test medium, for 7 days in a static or semi-static system to evaluate the growth rate inhibtion or yield inhibition.
TEST SYSTEM
Lemna minor (SIS medium), Lemna gibba (AAP 20X) medium.
A toxic reference substance is tested twice a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (3 replicates/concentration or control) with plants with a total of 9 to 12 fronds/replicate
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration (100 mg/L or at solubility limit) of the test substance and 1 untreated control (at least 6 replicates/concentration or control) with plants with a total of 9 to 12 fronds/replicate
Dose-response test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and
1 untreated control (3 replicates/concentration or control) with plants with a total of 9 to 12 fronds/replicate.
Analytical checks, to verify the exposure concentrations in the medium, are performed for static test at time 0 and at time 7 days on control and on each test substance sample and for semi-static test at time 0, at 2 days, at 5 days and at 7 days on control and on each test substance sample.
The analysis are performed using a method validated according to SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 and SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance documents.
ENDPOINTS
Inhibition of the growth rate and of the yield: EC10, EC20, EC50, NOEC/LOEC after 7 days calculated by the fronds number. Dry or fresh weight.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 221 (23rd March 2006) – Lemna sp. growth inhibition test.
OECD Series on Pesticides, Number 67: “OECD guidance to the environmental safety evaluation of microbial biocontrol agents” (17th February 2012).
Environmental Canada, EPS 1/RM/44: “Guidance Document for Testing the Pathogenicity and Toxicity of New Microbial Substances to Aquatic and Terrestrial Organisms” (March 2004).
SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 (16/11/2010) – Guidance document on pesticide residue analytical methods.
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
OECD TG 238: Sediment-free Myriophyllum spicatum Toxicity test
Myriophyllum spicatum (aquatic plant in house breeding at B.T.) is cultured in Modified Andrews’ Medium. Fresh lateral branches from pre-culture shortened to 2.5 cm from base are assigned randomly to the test vessels. The test, under static or semi-static conditions, ends after 14 days of exposure to different concentrations of the test substance. Total shoot length and main shoot length, fresh and dry weight are measured.
TEST SYSTEM
Myriophyllum spicatum
A toxic reference substance is tested twice a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes from 5 to 7 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (5 replicates/concentration or control) with one 2,5 cm lateral branch with apical meristem and one end/replicate.
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration (100 mg/L or at solubility limit) of the test substance and 1 untreated control (10 replicates/concentration and 20 replicates for the control) with one 2,5 cm lateral branch with apical meristem and one end/replicate.
Dose-response test includes from 5 to 7 concentrations of the test substance and
1 untreated control (5 replicates/concentration and 10 replicates for the control) with one 2,5 cm lateral branch with apical meristem and one end/replicate.
Analytical checks, to verify the exposure concentrations in the medium, are performed for static test at time 0 and at 14 days on control and on each test substance sample.
For semi-static test the analysis are carried out at time 0, at 7 days (in spent and fresh solutions) and at 14 days on control and on each test substance sample.
The analysis are performed using a method validated according to SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 and SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance documents.
ENDPOINTS
Specific growth rate and yield for each measured variable: EC50 at 14 days as the main endpoint and as other endpoints: EC10, EC20, LOEC/NOEC.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 238 (26th September 2014) – Sediment-free Myriophyllum spicatum toxicity test.
SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 (16/11/2010) – Guidance document on pesticide residue analytical methods.
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
OECD TG 239: Water-sediment Myriophyllum spicatum Toxicity test
Shoot apices of healthy non-flowering plants of Myriophyllum spicatum (in house breeding at B.T.) are potted in standardised, arificial sediment, supplemented with additional nutrients and manteined in Smart and Barko medium.
After roots formation, plants are exposed to a series of test concentrations added to the water column. Alternatively exposure via sediment may be simulated by spiking the artificial sediment with the test substance and transplanting plants into the treated sediment. The test is carried out under static conditions. Total shoot length, main shoot length, fresh and dry weight are measured.
TEST SYSTEM
Myriophyllum spicatum
A toxic reference substance is tested twice a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.
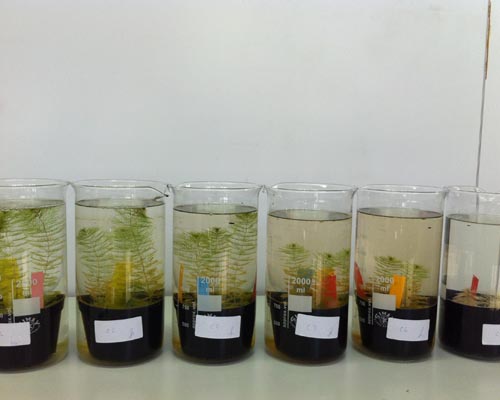

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (2 replicates/concentration and 3 replicates for the control) with 3 shoots per pot and 1 pot/replicate.
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration (100 mg/L or at solubility limit) of the test substance and 1 untreated control (6 replicates/concentration or control) with 3 shoots per pot and 1 pot/replicate.
Dose-response test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and
1 untreated control (4 replicates/concentration and 6 replicates for the control) with 3 shoots per pot and 1 pot/replicate.
Analytical checks, to verify the exposure concentrations in the medium, are performed for static test at time 0 and at 14 days on control and on each test substance sample. Where relevant or required, samples to be analyzed include: water, pore water and sediment.
The analysis are performed using a method validated according to SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 and SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance documents.
ENDPOINTS
Specific growth rate and yield for each measured variable: EC50 at 14 days as the main endpoint and as other endpoints: EC10, EC20, LOEC/NOEC.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 239 (26th September 2014) – Water-sediment Myriophyllum spicatum toxicity test.
SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 (16/11/2010) – Guidance document on pesticide residue analytical methods.
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
Aquatic invertebrates
OECD TG 202: Daphnia sp., Acute Immobilization test
Young daphnids (in house breeding at B.T.), not older than 24 hours at the start of the test, are exposed to a range of concentrations of the test substance in the test medium (ISO water) for 48 hours in static or semistatic conditions. The exposure is carried out under controlled conditions of temperature and light cycle. The immobilization is measured at 24 and 48 hours and compared with the control.
TEST SYSTEM
Daphnia magna
A toxic reference substance is tested twice a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.
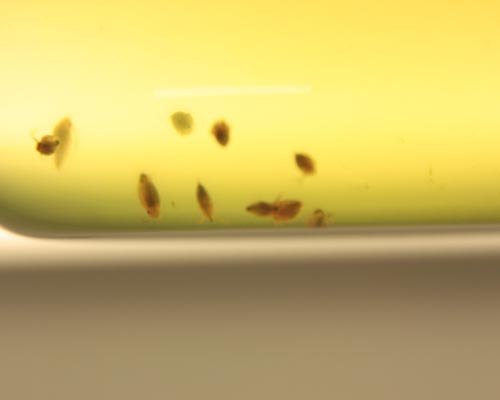

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (4 replicates/concentration or control) with 5 daphnids/replicate
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration (100 mg/L or at solubility limit) of the test substance and 1 untreated control (4 replicates/concentration or control) with 5 daphnids/replicate
Dose-response test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and
1 untreated control (4 replicates/concentration or control) with 5 daphnids/replicate
Analytical checks, to verify the exposure concentrations in the medium, are performed for static test at time 0 and at time 48 hours on control and on each test substance sample and, for semi-static test at time 0, time 24 hours and time 48 hours on control and on each test substance sample.
The analysis are performed using a method validated according to SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 and SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance documents.
ENDPOINTS
Immobilization: EC50 at 48 hours as the main endpoint and as other endpoints: EC10, EC20, LOEC/NOEC.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals, No. 202 (13th April 2004) – Daphnia sp., acute immobilization test.
SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 (16/11/2010) – Guidance document on pesticide residue analytical methods.
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
OECD TG 211: Daphnia magna Reproduction test
Young female Daphnia (the parent animals, in house breeding at B.T.), aged less than 24 hours at the start of the test, will be exposed at determinate concentrations of test substance in the test medium (M4) for a period of 21 days in semi-static conditions.
At the end of the test, the reproductive output of the parent animals will be evaluated based on the total number of living offspring produced.
TEST SYSTEM
Daphnia magna
A toxic reference substance is tested twice a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.
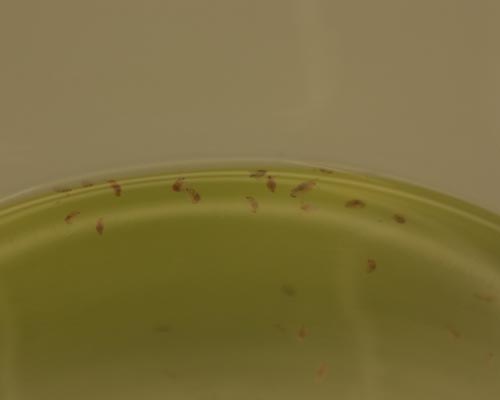

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding for acute immobilization test is carried out with at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (4 replicates/concentration or control) with 5 daphnids/replicate
Range finding for reproduction test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (10 replicates/concentration or control) with 1 daphnid/replicate
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration (as 10 mg/L or 100 mg/L) of the test substance and 1 untreated control (10 replicates/concentration or control) with 1 daphnid/replicate
Dose-response test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and
1 untreated control (10 replicates/concentration or control) with 1 daphnid/replicate
Analytical checks, to verify the exposure concentrations in the medium, are performed at time 0, 3 times per week (in spent and fresh solutions) and at 21 days on control and on each test substance sample.
The analysis are performed using a method validated according to SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 and SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance documents.
ENDPOINTS
Reproduction: EC10, EC20, EC50 and LOEC/NOEC.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 211 (2nd October 2012) – Daphnia magna reproduction test.
OECD Series on Pesticides, Number 67: “OECD guidance to the environmental safety evaluation of microbial biocontrol agents” (17th February 2012).
Environmental Canada, EPS 1/RM/44: “Guidance Document for Testing the Pathogenicity and Toxicity of New Microbial Substances to Aquatic and Terrestrial Organisms” (March 2004).
SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 (16/11/2010) – Guidance document on pesticide residue analytical methods.
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
OECD TG 235: Chironomus sp., Acute Immobilization test
First instar Chironomus riparius larvae (in house breeding at BT) are exposed to a range of concentrations of the test substance in the test medium (M4 medium) for a period of 48 hours. The exposure is carried out under controlled conditions of temperature and light cycle. The immobilization is recorded at 24 and 48 hours and compared with the control.
TEST SYSTEM
Chironomus riparius
A toxic reference substance is tested twice a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.
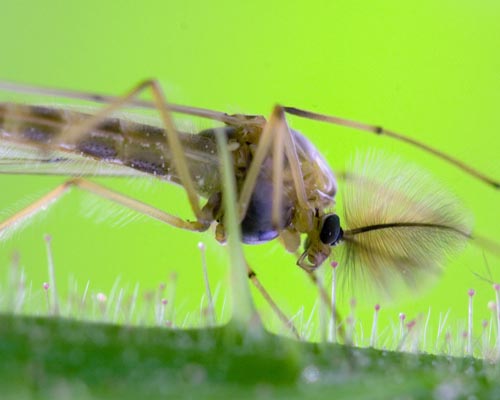

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (2 or 4 replicates/concentration or control) with 5 larves/replicate
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration (100 mg/L or at solubility limit) of the test substance and 1 untreated control (4 replicates/concentration or control) with 5 larves/replicate
Dose-response test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and
1 untreated control (4 replicates/concentration or control) with 5 larves/replicate
Analytical checks, to verify the exposure concentrations in the medium, are performed at time 0 and at time 48 hours on control and on each test substance sample.
The analysis are performed using a method validated according to SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 and SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance documents.
ENDPOINTS
Immobilization: EC50 at 48 hours as the main endpoint and as other endpoints: EC10, EC20, LOEC/NOEC.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 235 (28th July 2011) – Chironomus sp., acute immobilization test.
SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 (16/11/2010) – Guidance document on pesticide residue analytical methods.
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
OECD TG 218: Sediment-water Chironomid toxicity test using spiked sediment
First instar Chironomus riparius larvae (in house breeding at BT) are exposed to a concentration range of the test substance in sediment/water system, for 28 days. The test substance is spiked into the sediment and first instar larvae are subsequently introduced into test beakers in which the sediment and water concentrations have been stabilised. The exposure is carried out under controlled conditions of temperature and light cycle. Chironomid emergence and development rate is measured at the end of the test and compared with the control. Larval survival and weight may also be measured after 10 days if required (using additional replicates as appropriate).
TEST SYSTEM
Chironomus riparius
A toxic reference substance is tested twice a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.
STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (1 replicate/concentration or control) with 20 larves/replicate
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration (1000 mg/Kg) of the test substance and 1 untreated control (6replicates/concentration or control) with 20 larves/replicate
Dose-response test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and
1 untreated control (4 replicates/concentration or control) with 20 larves/replicate
Analytical checks, to verify the exposure concentrations (where relevant or required samples include water, pore water and sediment), are performed at time 0 and at time 28 days on control and on each test substance sample.
The analysis are performed using a method validated according to SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 and SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance documents.
ENDPOINTS
Emergence, development rate: EC50 at 28 days as the main endpoint and as other endpoints: EC15, LOEC/NOEC.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 218 (13th April 2004) – Sediment-water Chironomid toxicity test using spiked sediment.
SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 (16/11/2010) – Guidance document on pesticide residue analytical methods.
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
OECD TG 219: Sediment-water Chironomid toxicity test using spiked water
First instar Chironomus riparius larvae (in house breeding at BT) are exposed to a concentration range of the test substance in sediment/water system, for 28 days. The test starts by placing first instar larvae into the test beakers containing the sediment/water system and subsequently spiking the test substance into the water. The exposure is carried out under controlled conditions of temperature and light cycle. Chironomid emergence and development rate is measured at the end of the test. Larval survival and weight may also be measured after 10 days if required (using additional replicates as appropriate).
TEST SYSTEM
Chironomus riparius
A toxic reference substance is tested twice a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (1 replicate/concentration or control) with 20 larves/replicate
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration of the test substance and 1 untreated control (6 replicates/concentration or control) with 20 larves/replicate
Dose-response test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and
1 untreated control (4 replicates/concentration or control) with 20 larves/replicate
Analytical checks, to verify the exposure concentrations (where relevant or required samples include water, pore water and sediment), are performed at time 0 and at time 28 days on control and on each test substance sample.
The analysis are performed using a method validated according to SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 and SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance documents.
ENDPOINTS
Emergence, development rate: EC50 at 28 days as the main endpoint and as other endpoints: EC15, LOEC/NOEC.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 219 (13th April 2004) – Sediment-water Chironomid toxicity test using spiked water.
SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 (16/11/2010) – Guidance document on pesticide residue analytical methods.
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
Fish
OECD TG 203: Fish, Acute Toxicity test
The fishes are exposed to the test substance for 96 hours under static or semi-static conditions. Temperature is controlled and from 12 to 16 hours photoperiod applied. Mortalities are recorded at 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours and the concentration which kill 50% of the fishes determined.
TEST SYSTEM
Oncorhynchus mykiss
A toxic reference substance is tested twice a year to check the sensitivity of the organisms.

STUDY DESIGN
Range finding test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (7 replicates/concentration or control) with 1 fish/replicate.
Limit test is carried out with 1 concentration (100 mg/L or at solubility limit) of the test substance and 1 untreated control (7 replicates/concentration or control) with 1 fish/replicate.
Dose-response test includes at least 5 concentrations of the test substance and 1 untreated control (7 replicates/concentration or control) with 1 fish/replicate.
Analytical checks, to verify the exposure concentrations in the medium, are performed for static test at time 0 and at time 96 hours on control and on each test substance sample.
For semi-static test the analysis are carried out at time 0, 24 hours, 48 hours, 72 hours (in spent and fresh solutions) and at 96 hours on control and on each test substance sample.
The analysis are performed using a method validated according to SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 and SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 guidance documents.
ENDPOINTS
Mortality: LC50 at 96 hours as the main endpoint and as other endpoints: LC10, LC20, LOEC/NOEC.
Study includes GLP management and reporting.
REFERENCES AND GUIDELINES
OECD Guideline fo Testing of Chemicals, No. 203 (17th July 1992) – Fish, acute toxicity test.
SANCO/825/00 rev. 8.1 (16/11/2010) – Guidance document on pesticide residue analytical methods.
SANCO/3029/99 rev. 4 (11/07/2000) – Residues: guidance for generating and reporting methods of analysis in support of pre-registration data requirements for Annex II (Part A, section 4) and Annex III (Part A, section 5) of Directive 91/414.
Study finder
Scientific Contact
Sabrina Mantilacci
E-mail: mantilacci@biotecnologiebt.it
Phone: +39 075 895 0045 – Ext. 252
Business Contact
Katy Lazzari
E-mail: klazzari@biotecnologiebt.it
Phone: +39 075 895 0045 – Ext. 246
Discover the other Expertise
Didn’t find what you are looking for? Send us a message!
Fill in the form with the required information (*).
Our team will be happy to provide all the necessary support with regard to your request.


 English
English Italian
Italian